How to Import and Export BPMN Files
Step-by-step guide to importing and exporting BPMN files in ProcessMind, plus details on supported BPMN elements.
Creating a BPMN diagram starts with understanding your process at a high level, then gradually adding detail. Here is a practical, beginner-friendly approach to building a BPMN diagram. Remember, there is no single right way. Feel free to adapt these steps to fit your needs!
Identify Essential Steps: Start by outlining the main steps in your process, including where it begins and ends. For example, in an order process, key actions might include receiving the order, checking credit, fulfilling the order, and sending an invoice.
Explore Alternative Paths: Look for possible alternative routes or outcomes, such as what happens if an order cannot be completed. Use gateways to show these different paths in your diagram.
Add Pools and Swimlanes: Identify the main stakeholders, departments, or roles involved. Organize activities into pools and swimlanes to make responsibilities clear at a glance.
Show Message Flows: Add any important messages exchanged between pools or within the same pool. This helps you visualize how information moves through your process.
Include Artifacts and Details: Attach relevant documents, notes, or actors to each step. If a step contains several smaller actions, consider making it a subprocess for clarity.
Plan for Errors: Think about what could go wrong and add error-handling steps or events to your diagram. This makes your process more robust and realistic.
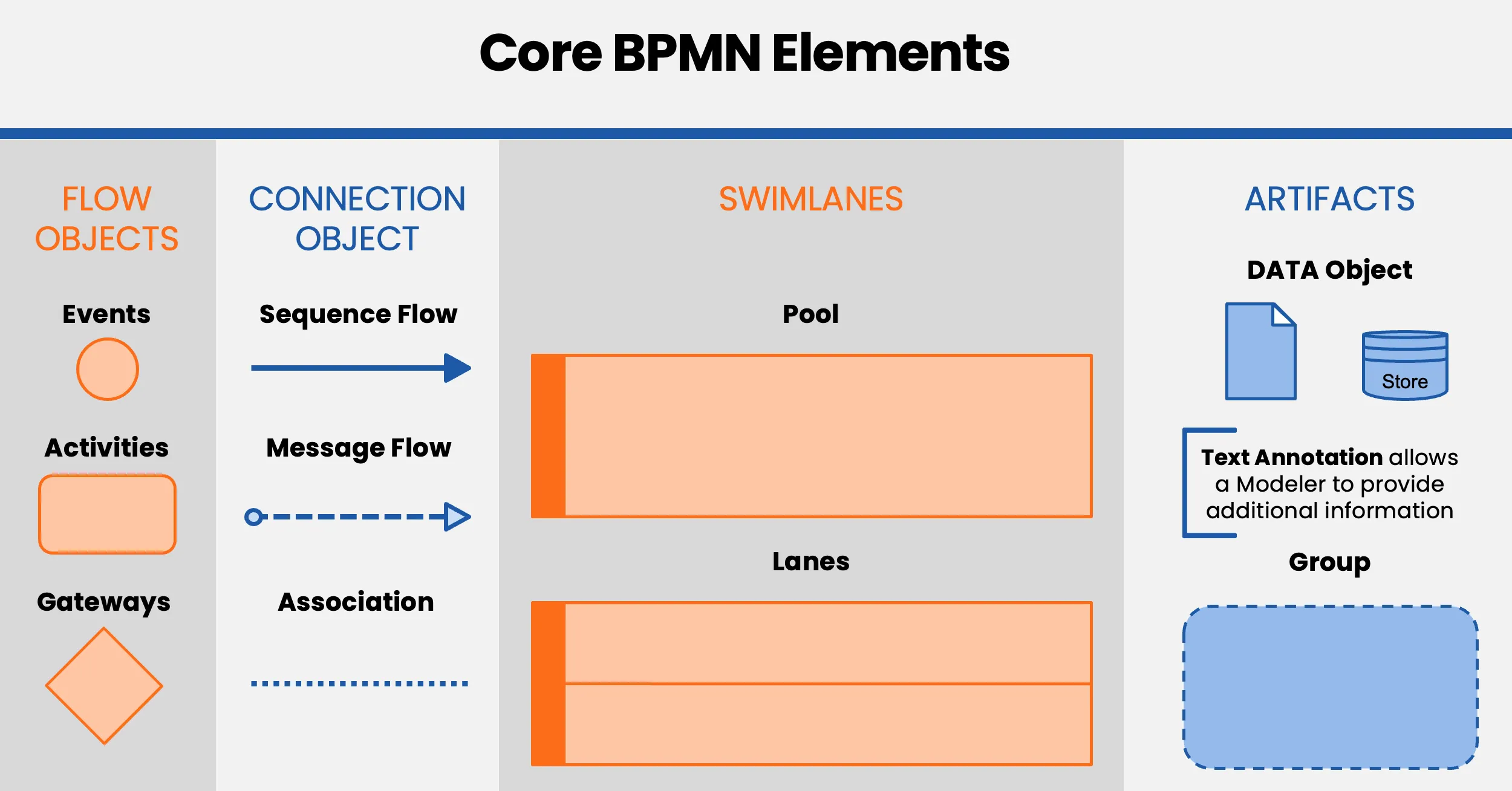
When you understand these core elements and how they work together, you will be able to create BPMN 2.0 diagrams that truly reflect your business processes.
BPMN 2.0 is not just a technical standard. It is a practical tool that can transform how you manage and improve your business. With its clear, visual approach, BPMN 2.0 makes it easier to communicate, spot opportunities for improvement, and streamline your operations.
If you are curious to learn more, check out the official BPMN website (https://www.bpmn.org/) or explore our additional resources below.
Do you want to dive deeper into the building blocks of BPMN 2.0 diagrams and discover how they can help you streamline your business processes? Click the links below to keep learning.
ProcessMind brings together process mining, process design, and process simulation to help you manage your business processes from start to finish. With our platform, you can monitor, analyze, and optimize your workflows. This unlocks new levels of efficiency and productivity.
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.